What is Thermoplastic Polymer?
Thermoplastic is a Type of Polymer, which is called as Thermoplastic Polymer that go through distinct manufacturing processes like Injection Molding, Blow Molding, Thermoforming, etc., and have different qualities based on the component elements and manufacturing method. The word thermoplastic refers to “how a material is or may be treated when the temperature is altered”. Thermoplastic is also called as Thermosoft Plastic. These type of polymers consists high Molecular Weight.

Also Read:
- 3D Printing Process – Its Types, Parts, Advantages, Disadvantages, Applications – FAQ’s
- Types of Printing Process and Machines – Their Working – And More
Additionally, a thermoplastic is a polymeric material that is composed of polymer resins that turns into flexible after heating and rigid when cooled. These materials are readily recyclable and exhibit no chemical property changes when heated up to their melting point or cooled repeatedly. When these thermosoft plastics are heated, their physical properties change, transforming into a homogeneous liquid that can be mold and resized. Thermoplastics are polymers that are linear or slightly chained. They have intermolecular forces, which attract Elastomers and Fibers.
The following are some of the qualities of thermoplastics that make them a viable alternative material:
- They have the capacity to endure caustic materials and conditions.
- Being ability to transport goods at high temperatures (hot or cold).
- Their versatility in handling almost any form of fluid conveyance application.
Table of Contents
More About Thermoplastics
- A Thermoplastic or Thermosoft Plastic is a polymer composite substance that may be molded or pliable at a certain temperature. Then the solidification of thermoplastic occurs when it cools. Furthermore, thermoplastics have a large molecular weight. They assume the shape of the mold into which they are injected as melt and cool to solidify into the desired shape when processed, often by Injection Molding or Blow-Molding procedures.
- The reversibility of thermoplastics, or their capacity to be reheated, and shaped, which is an important feature. This enables further processing of the same material, even after it has been produced as a solid. Extrusion, thermoforming, and injection molding all rely on similar material behaviour.
- They are just like every type of materials; do have limits. Extremely high temperatures may cause the material to soften, distort, and lose some of its physical qualities.
- When heat is applied to thermosoft plastic pellets, they soften and become more fluid. Furthermore, their curing process is fully reversible. The reason for this is that there is no chemical bonding taking place in this procedure.
- Thermoplastic Re-Molding and Recycling are simple processes that have no detrimental influence on the material’s physical qualities. Sometimes it is necessary to choose between thermoset and thermoplastic composites. Simply said, thermoplastic matrix composites are less brittle and harder than thermosets, resulting in superior damage limitation and shock resistance.
- Numerous thermosoft plastic polymers provide a variety of performance advantages. They are notable for their strong strength, excellent bendability, and good shrink resistance. Furthermore, they may effectively serve a variety of low-stress applications such as high stress mechanical components or plastic bags.
Types of Thermoplastic Polymers
There are different types of Thermoplastics; they are
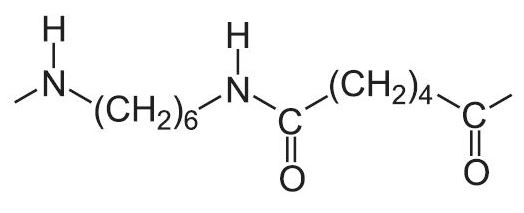
- Polyamide (Nylon)
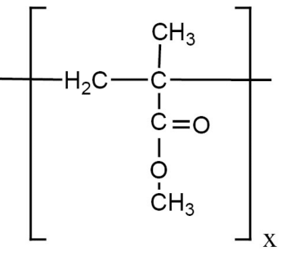
- Poly-Methyl Methacrylate (PMMA, Acrylic)
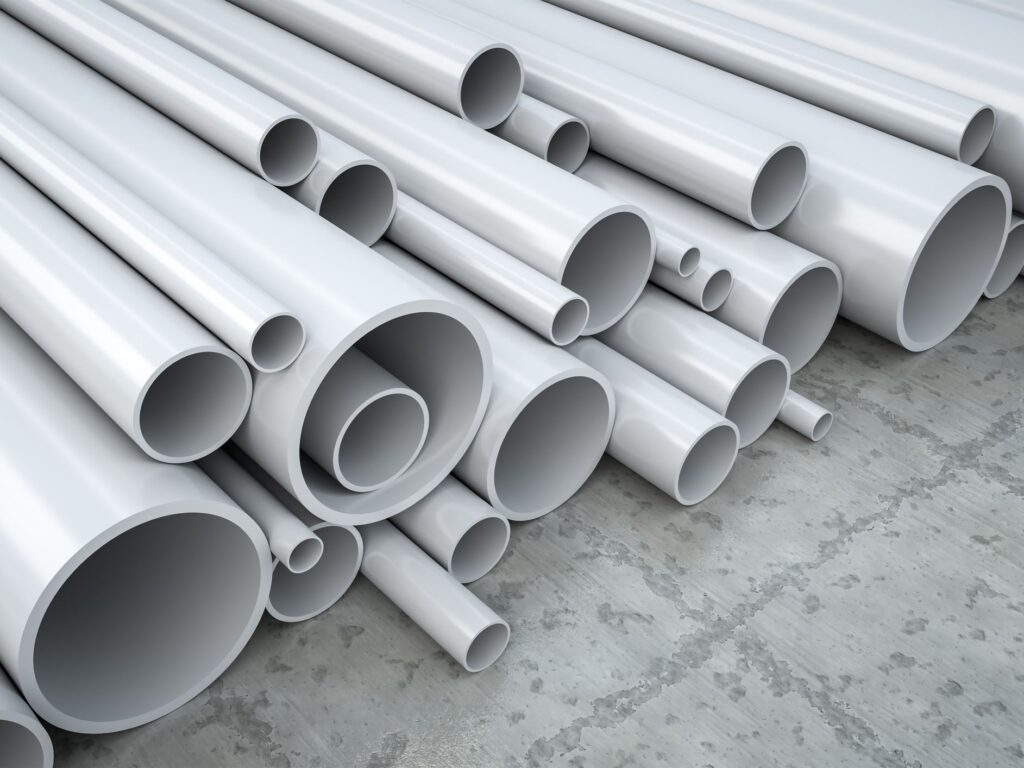
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)

- Polypropylene

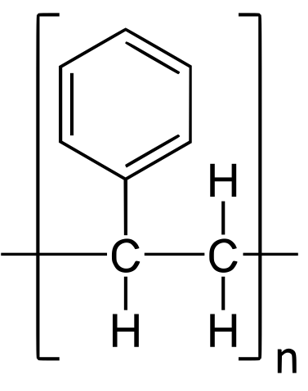
- Polystyrene (PS)
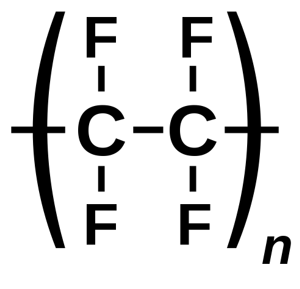
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, Teflon)
- Low-density Polythene (LDPE)
- High-density Polythene (HDPE)
Properties of Types of Thermoplastic Polymers with Applications
| Type of Thermoplastic | Properties | Applications |
| Polyamide (Nylon) | Tough Reasonably Durable Material | Utilized to Manufacture of Power Tool Cases, Curtain Rails, Bearings, Gear Components, And Clothing. |
| Poly-Methyl Methacrylate (PMMA, acrylic) | Stiff Resilient And Hard Plastic That Polishes To A Shine | Signage, Aero plane Fuselage, Windows, Bathroom Sinks, and Bathtubs. |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Tough And Long-Lasting Material | Pipes, Floors, Cupboards, Toys, And Regular Home And Industrial Fittings. |
| Polypropylene | Lightweight Yet Robust Material With Good Chemical Resistance, | Used For Medical & Laboratory Equipment String Rope, And Cooking Utensils. |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Lightweight Stiff Hard Brittle Waterproof Material | Mostly Used For Rigid Packing |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, Teflon) | Robust And Flexible | Utilized For Nonstick Cooking Utensils, Machine Components, Gears, And Gaskets. |
| Low-density Polythene (LDPE) | Tough Reasonably Soft And Chemically Resistant | Used In Packaging, Toys, Plastic Bags, And Film Wrap. |
| High-density Polythene (HDPE) | Stiff Rigid Chemical-Resistant Substance. | Plastic Bottles And Household Items Casings. |
Processing of Thermoplastic Polymers
The Thermoplastic Polymers can be processed using few manufacturing techniques, they are
- Extrusion Molding
- Injection Molding
- Thermoforming, And
- Vacuum Forming
The basic and normal process that involved in every type of manufacturing technique will be
Step 1:
Firstly, the Fine Grained Materials is supplied into the Injection Molding or Blow Molding, Thermoforming or any other type of processing, often in the shape of spherical granules almost 3 mm in diameter. These granules are then heated to its melting temperature, which necessitates extremely high temperatures.
Step 2:
Thermoplastics are very efficient thermal insulators so the cooling takes longer during the curing process than conventional polymers. As a result, quick cooling is used to generate a high output rate; often by spraying with cold water or immersing in water baths.
Also Read:
- Electric Bicycle – Green Technology – Their Parts, Working, Advantages, Applications – And More
- Types of Electric Bicycle – Their Parts, Working, Advantages, Applications – And Many More
Step 3:
Then Cold Air is blasted over the surface of thermosoft plastic films to cool them. The plastic shrinks when it cools whereas; shrinkage rates ranging from 0.6 percent to 4 percent depending on the type.
The frequency of cooling and shrinkage has a particular influence on the Crystallization and internal structure of the material, and that is why the shrinkage rate is always given for thermoplastics. Due to this process, every component is processed by using the Thermoplastic Polymers.
Advantages of Thermoplastic Polymers
The advantages of Thermoplastic Polymers are
- The major benefit of thermoplastics is their versatility.
- Thermosoft Plastic Polymers are lightweight, which can be found at the places where Injection Molding, Blow Molding Machines, etc. are used.
- They are high-strength materials with minimal production costs.
- Thermoplastic components are extremely simple to produce in great volume and accuracy.
Disadvantages of Thermoplastic Polymers
The disadvantages of Thermoplastic Polymers are
- Thermoplastics are susceptible to deterioration in resistance to organic solvents, hydrocarbons, and extremely polar solvents.
- Creep is a phenomenon that happens when a material expands and weakens; as a result of long-term stress loading.
- Under high-stress circumstances, other thermosoft plastics such as composites can fracture rather than deform.
- The fundamental drawback of employing thermoplastics over materials such as metal is their low melting point.
- When some types of low-quality thermoplastics are exposed to the sun for long periods of time, they can melt.
Pros and Cons of Thermoplastic Polymer Materials
The Pros of Thermoplastic Polymers are
- Extremely adhesive to metal
- High recyclable
- Superb impact resistance
- Can be remolded and reshaped using Injection Molding, Blow Molding, Thermoforming, etc.
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Slip enhancement
- Detergent and chemical resistance
- Flexibility and elongation of the coating film
- Electrical insulation
- Chip resistance
- Aesthetically-superior finishes
- Superb corrosion resistance
The Cons of Thermoplastic Polymers are
- May soften when reheated
- They Can be more expensive than thermoset
Applications of Thermoplastics Polymers
The applications of Thermoplastic Polymers are
- Steel Pipe Systems are typically sensitive to rust or corrosion in polluted, acidic environments such as those present in modern cities, and so require particular corrosion prevention procedures. The expense of preserving steel pipe systems exposed to these hostile conditions can be prohibitively high. Thermoplastics are thought to be a good option for reducing these expenses.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) or Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) are common materials used to make these pipes. Polypropylene, PVDF, ABS, Nylon, and polyethylene are among the other materials used.
- Natural Gas is transported in polyethylene gas tanks for usage in household and commercial applications.
- High-pressure Polyethylene is another frequent use for thermoplastics, which is used to enclose stiff things such as electrical equipment.
- Low-pressure polyethylene is an extremely elastic material that is perfect for insulating electrical wires.
- Polyamide is most typically used in the manufacture of ropes and belts.
Conclusion
Thermoplastics are available in a variety of material alternatives and may be used for a variety of applications as long as the material’s limits are unlikely to cause product failure under the specified operating conditions. The fundamental characteristics of these materials remain the same; great adaptability and recyclability. When it comes to practical applications in the real world, you won’t find a greater example than the manufacture of plastics using these two techniques.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some of the advantages of thermoplastic resins?
Ans: The advantages of thermoplastic resins or thermosoft plastic resins include high strength, high shrink resistance, easy bendability, and the ability to serve low-stress applications effectively.
What does unsaturated polyester resin mean?
Ans: Unsaturated polyester resin is a form of thermosetting plastic, along with epoxy resin and phenolic resin. Most notably, unsaturated polyester resins are used in the production of plastic-reinforced fiberglass.
What are the properties of Thermoplastic Polymers?
Ans: According on the kind of resin, the properties of thermoplastics usually have great
- Strength
- Flexibility, and
- Resistant to shrinking (the polymer in melted liquid form).