What Is A Spring?
A Spring is a Mechanical Component as well as an Elastic Member whose primary function is to “deform under load and regain its original shape” when the load is removed. Because of its elasticity, the spring is not permanently deformed.
What Is A Load – The force applied by the spring is known as “load”, and can be measured in pounds, kilograms, or any other unit of force.
For example,
A Helical Spring made of steel can be expanded to twice its length without losing its elasticity property.
Most items we use on a daily basis contain springs, which are frequently invisible.
Some More Examples of this include…..
Turning on and off your lights, and even inserting your key into the front door to gain entry. But there are many types of springs, and each has certain advantages for certain uses.
Mostly, Springs are used in industrial applications such as
- Shock Absorbers
- In Toys
- Clocks to Store Energy and among so many other uses of springs.
Spring is used by every industry to meet their specific needs. According to various requirements, springs are available in various designs, shapes, and sizes.
What Are The Materials Used To Make Springs?
As said, Springs are used for different purposes so, same material will not work out for different types. So, different materials are used to make them. They are
- Stainless Steel
- Steel Alloys
- Nickel Alloys
- Copper Based Alloys
- Titanium Alloys
1. Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel is one of the materials that is commonly used for springs. This material is ideal for
- Higher Corrosion and
- Heat Resistance
Stainless steel comes in several different grades, each with its own properties, as well as types, namely
- Austenitic
- Martensitic and
- Precipitation Hardening.
This is a versatile alloy for springs and types of springs, which is used in a variety of markets that are including
- Architecture
- Art
- Aerospace
- Chemical processing
- Food Processing and
- Transportation, etc.
2. Steel Alloys
Alloy Steels have one or more elements added to improve their qualities like load bearing capacity and retain capacity. Alloy steels sometimes increase the
- Strength
- Toughness
- Resistance to Corrosion
- Capacity to be Hardened, and
- Hot hardness.
3. Nickel Alloys
Nickel is a Flexible Metal that can combine with a wide variety of other metals. Additionally, nickel alloys sometimes provide a high level of strength and toughness and continue to be dependable even in the most difficult situations, such as Chemical Plants or Oil Rigs. When Stainless Steel is not sufficient, Cobalt-Nickel Alloys are commonly selected. These alloys have remarkable
- Corrosion Resistance
- High Strength
- Durability, and
- Ductility
4. Copper-Based Alloys
The alloys made from Copper include
- Brass
- Bronze, and
- Beryllium.
These different kinds of copper are used to produce a wide range of springs, all of which have very different properties. Spring brass has a High Degree of Conductivity and will assist keep prices down. It is considered to have very poor Mechanical Quality.
5. Titanium Alloys
Titanium and other chemical elements are combined to create Titanium Alloys. They are separated into grades that differentiate between their features and advantages, such as Ductility and Formability.
Even though this material also has additional qualities like extreme corrosion resistance and heat resistance, it generally has a low weight. This material is frequently utilised in industries including
- Aerospace
- Medicine and
- The automobile because of its durability.
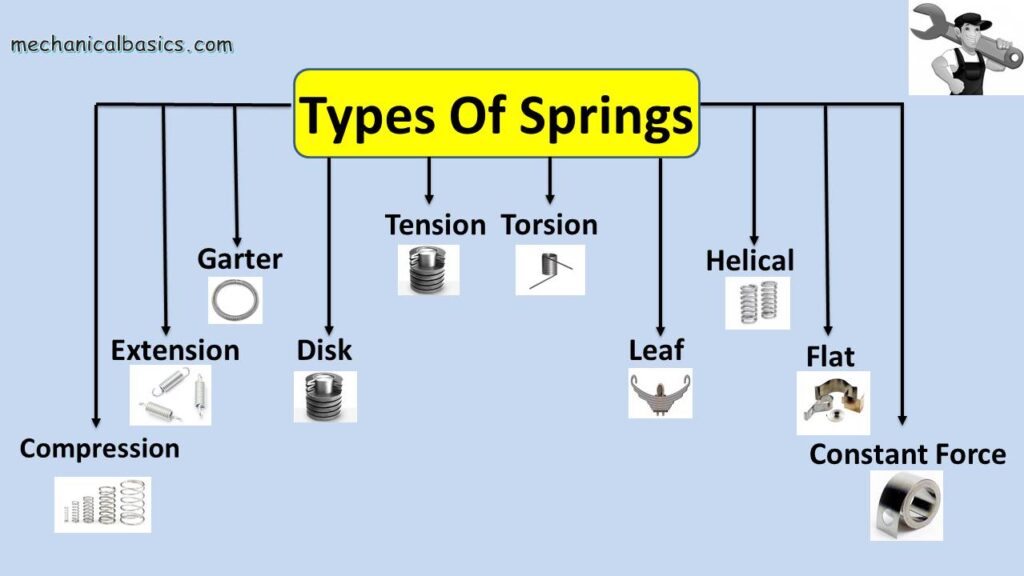
Types of Springs
There are different types of springs that are used in the domestic, industrial, etc. purposes and they are
- Helical Springs
- Compression Springs
- Extension Springs
- Torsion Springs
- Disk Springs
- Leaf Springs
- Flat Springs
- Tension Springs
- Garter Springs
- Constant Force Springs
1. Helical Springs

A Wire with a Circular Cross-Section is bent into the Shape of a Helix to create the Helical Spring.
Helical springs are classified into two types: They are
- Compression Springs and
- Tension Springs
An External Force has the potential to shorten a helical compression spring. The spring is compressed. An external force has the potential to stretch a helical spring. The spring is thus extended. The wire of a helical compression spring is not subject to compressive stress, even though that spring is in compression. Even when the spring is under tension, the wire of the helical spring is not pushed under tensile stress.
Torsional Shear Stresses are induced in the spring wire in both circumstances. Instead of referring to the stresses in the spring wire, compression and tension refer to the entire spring.
Advantages of Helical Springs
The advantages of Helical Springs are
- There is a long life expectancy for the helical springs.
- These springs were carefully and precisely developed for this purpose.
- Their dimensional stability is respectable.
- These springs are made of a strong material.
- The Tensile Strength of these springs is high.
Disadvantages of Helical Springs
The disadvantages of Helical Springs are
- Helical Springs are of High Cost compared to others
- There is an issue with Load Bearing too.
Applications of Helical Springs
The applications of Helical Springs are
These springs are perfect for usage in a variety of applications because they have a wide range of qualities and useful features. The following are a few typical uses or applications of helical springs
- Trampolines
- Mesh Doors
- Exercise Resources
- Toys
- Weapons
- Carburetors
- Pliers with Vise-Grip
- Assemblies for Garage Doors
2. Compression Springs

Compression Spring is the most common type of spring that we can see. They are also known as Coil Springs, which are mechanical devices that store energy and absorb forces when compressed and release them when relaxed. They are cylindrical, with a constant slope, round, oval, or square steel wires.
The pen is a perfect example of this type of spring. Whenever a pen is clicked, the spring is compressed, and when the pen is clicked once more, the spring releases the stored energy and returns to its initial condition.
These kinds of springs follow a particular law, known as Hooke’s Law. It implies that “a spring’s resistance to stretching or compression is proportional to its length”.
Advantages of Compression Springs
The advantages of Compression Springs are
- Compression Springs have some of the most prominent and amazing benefits in battery-operated products.
- Compression spring maintenance is not very necessary.
- This type of spring is Lightweight.
- Compression springs are generally made of steel or other less expensive metals.
Disadvantages of Compression Springs
The disadvantages of Compression Springs are
- Costly Springs
- Being crushed for a prolonged period of time, becomes weaker.
- With time, it loses shape and stability.
- Buckles as the axial load increases.
- Difficult to fix when damaged.
Application of Compression Springs
The applications of Compression Springs are
- Compression springs are utilised in a wide range of products, including car engines, massive stamping presses, large appliances like lawnmowers, electrical devices, cell phones, and delicate instrumentation devices.
- Anywhere a push-button is needed, the simplest installation is there. Applications requiring a minimal solid level and higher surge resistance frequently use compression springs.
3. Extension Springs

- Trampolines are among the most popular applications for Extension Springs. The springs on a trampoline are expanded as you bounce on it, but its secret is that the initial tension within the spring releases the energy it has been holding onto, causing the trampoline user to bounce in the air.
- Extension Springs resist a pulling force while simultaneously absorbing and storing energy. On both ends, extension springs are attached to additional parts. The extension spring makes an effort to reunite these parts when they separate. These springs resist a pushing force while absorbing and storing energy.
- How tightly an extension spring is wound depends on its initial tension. For a specific application’s load needs, this initial tension can be changed. On the ends of extension springs, loops, eyes, or other interface patterns are used to connect to the parts they link. They are commonly used to provide return force to stretched, activated components.
Advantages of Extension Springs
The advantages of Extension Springs are
- Lack of bends, the potential for central power transfer.
- Its lack of friction as a result of the removal of guide components like sleeves or mandrels.
Disadvantages of Extension Springs
The disadvantages of Extension Springs are
- The size of the installation area, the sensitive point at the loop connection, and the subsequent complete loss of spring force after a loop break are all drawbacks of the extension spring.
- There are additional situations when several extension spring systems are used. The most typical application example uses parallel-connected garage door spring components to hold objects with a higher mass in place with constant stresses and spring moments.
Application of Extension Springs
The applications of Extension Springs are
- Exterior and interior of cars
- Assemblies for garage doors
- Clamp-on pliers
- Carburetors
- Trampolines
- Washing equipment
- Toys for farm equipment
4. Torsion Springs

Torsion Springs is one of the types of springs. Compression and Extension Springs function similarly, but torsion springs work little differently. A Torque or Twisting Motion is used to apply the load to a torsion spring, as opposed to an Axial Force. In other words, when this spring is twisted, it provides resistance and forces the spring to return to its starting position.
Clothes Pegs are a typical application for torsion springs. The peg opens up at the bottom when squeezed and can be fastened to a laundry line. The torsion spring is twisted during this squeezing operation and stores energy. Once you hang it up on the clothes line and relax the pressure on the peg, the peg closes as it should once the stored energy is released.
Advantages of Torsion Springs
The advantages of Torsion Springs are
- They are long-lasting and offer good value for the money because they are durable.
- Simple to use – for example, torsion springs in vehicles can be easily adjusted.
- Torsion springs are generally limited, which enables them to fulfil a variety of applications even in small spaces.
Disadvantages of Torsion Springs
The disadvantages of Torsion Springs are
- In the case of car suspensions, they are unable to fulfil the required functionality.
- Spring Rust is another disadvantage with Torsion Spring.
Application of Torsion Springs
The applications of Torsion Springs are
The applications of Torsion springs can be seen in
- Motion Traces
- Switches That Rock
- Hinge Doors
- Switches
- Vehicle Starters
5. Disk Springs

- Disk Springs, also known as Belleville Springs. They are great for high-load applications, especially in closed areas.
- A convex disk is used to create this spring, with the outer edge being forced in the opposite direction as the disk’s centre. It produces a powerful spring force as a result, within a limited range of motion.
- Disc springs handle heavy loads with relatively minimal deflection while having a lower solid height than typical helical-designed springs. Due to their adaptability, these springs are used in commercial and plant applications.
- Additional categories can also be used to categorise disk springs. Disc springs can store a lot of energy and last a very long time. Using these springs conserves space. It offers superior shock absorption and energy dissipation.
Advantages of Disk Springs
The advantages of Disk Springs are
- Disc springs have a great capacity for storing energy and a long lifespan.
- It saves room to use these springs.
- Both energy dissipation and shock absorption are good.
Disadvantages of Disk Springs
It is difficult to ensure load deviation in a disk spring.
Application of Disk Springs
The applications of Disk Springs are
- Brake Plate
- Valve for High Pressure
- Braking Systems
- Actuators For Valves
- Joints With Live Loads
6. Leaf Springs
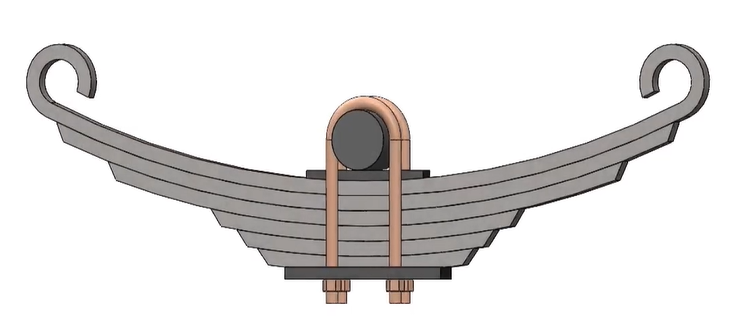
- A Multi-Leaf Spring is commonly used for truck and railway carriage suspension.
- It is made up of a number of flat plates that are usually semi-elliptical. It is called Spring Leaves when the flat plates are used.
- There is a maximum length for the leaf at the top. A master leaf is the tallest leaf in the plant. The lengths of the leaves differ. As you move from the top leaf to the lowest leaf, the length gradually gets shorter.
- It has a bend at each end that creates the spring eye. To secure the leaf spring to the car body, two bolts are threaded through these eyes. Two U-bolts, along with a centre clip, are used to secure the leaves together. Rebound clips are used to keep the leaves aligned and to prevent lateral leaf displacement during operation.
- The axle at the centre supports the leaf spring. In addition to the master leaf, multi-leaf springs are equipped with one or two additional full leaves. The master leaf is stacked between the graduated-length leaves and the extra full-length leaves.
- In order to withstand the transverse shear force, extra full-length leaves are provided.
Advantages of Leaf Springs
The advantages of Leaf Springs are
- The axle is held in place without the need for a separate connection due to the extremely straightforward and durable construction of the suspension.
- The position of the rear axle reduces extra weight and expenses.
- For commercial vehicles, leaf springs are the best choice because they are able to support the chassis’ weight.
- They additionally manage axle damping.
Disadvantages of Leaf Springs
The disadvantages of Leaf Springs are
- They aren’t always the simplest to install, but there is a straightforward procedure to follow that greatly simplifies things.
- The springs have a tendency to droop and lose their shape over time. Uneven flex can change the vehicle’s cross weight, which may have a minor impact on handling.
- Acceleration and braking torque might result in wind-up and vibration. Additionally, the wind-up may result in rear-end squatting and nose-diving.
Application of Leaf Springs
The applications of Leaf Springs are mostly found in the Automobile Suspension.
7. Flat Springs

Flat Springs are designed differently than the previous springs, yet they fulfil the same purpose.
- Flat Springs are essentially tiny metal strips that can store mechanical energy when they are bent by a force.
- High carbon steels, nickel, beryllium-copper, and a variety of other metals can be used to create them.
Advantages of Flat Springs
The advantages of Flat Springs are
- The fall in work height is a result of flat wire’s smaller vertical dimension than round wire.
- Flat wire springs are versatile springs that are frequently used in a wide range of industrial applications.
- Flat wire springs are more strongly constructed to enclose heavy impact stress.
Disadvantages of Flat Springs
The disadvantage of Flat Springs is its size. It requires more space to install.
Application of Flat springs
The applications of Flat Springs are
- Electronic connectors
- Spring leaf
- Wheel washers
- Hold-downs \Clips \Shims
8. Tension Springs

- Round or Oval Steel Wires are used to create tension springs or coil springs.
- These springs can be shaped in the cold forming process by winding them around or with highly automated spring coiling equipment using multiple wire guide pins.
- In addition to cylindrical designs, conical or barrel-shaped tension springs with a linear characteristic are produced.
- In addition to a progressive spring quality, a longer spring service life is achieved with conically tapered spring ends.
Advantages of Tension Springs
The advantages of Tension Springs
- Tension springs are extremely durable.
- Tension springs are specifically created with great precision.
- Their dimensional stability is excellent.
- These springs are made of sturdy material.
- These springs have a strong tensile capacity.
Disadvantages of Tension Springs
The disadvantage of Tension Springs is its limited Elasticity.
Application of Tension Springs
The applications of Tension Springs are
- Weighing Equipment
- Dishwasher Door
- Pliers with Vise-Grip
9. Garter Springs

- Garter springs are Circular Helical Springs with their ends connected to create a high radial force.
- They are made from extension springs and offer a radial force that contracts.
- One end of the garter spring can be conjoined to form a nib joint with the other end, or it can be wrapped so that it can be hooked onto the other end to form a loop.
- The ability to cut and construct your garter springs as needed is extremely helpful for regular weights or diameters. They can also be delivered pre-assembled into loops or in lengths.
Advantages of Garter Springs
The advantages of Garter Springs are
- Despite their strength, these springs are extremely durable.
- Garter springs can handle fluctuations in volume, pressure, temperature, and viscosity easily.
Disadvantages of Garter Springs
Expensiveness is the main disadvantage of Garter Springs.
Application of Garter Springs
The applications of Grater Springs are
- Seals for air conditioners
- Off-road wheel seals
- Diesel engine seals
10. Constant Force Springs

- The Constant Force Springs produce a force that is almost constant, as opposed to proportional.
- Constant force springs often take the shape of a thin sheet of metal tightly wound around a drum. Unlike the other springs mentioned above, constant force springs disobey Hooke’s Law.
Advantages of Constant Force Springs
The advantages of Constant Force Springs are
- Flexible range of motions.
- Little space required
- Creates a Balancing Effect.
Disadvantages of Constant Force Springs
Deformation modes are restricted by the appearance of “necking” instabilities, which is one of its disadvantages.
Application of Constant Force Springs
The application of Constant Force Springs
- Exercise equipment
- Counter balances
- Cable retractors
- Furniture cabinet parts
- Appliances
- Space Craft
Conclusion
Springs are a core part of every product that moves. They have the ability to store and release energy when compressed and expanded. Knowing the many types of springs used nowadays can help you choose the best spring. Depending on the materials used, the design, and the manufacturing method, each spring has its own unique qualities and features.
Therefore, it is best to take the above aspects into account when deciding to create a spring for your product.