What Are Electronic Components?
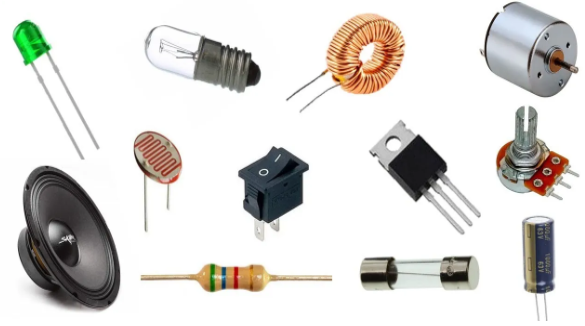
Electronic components are considered basic building blocks for electrical circuits. They perform operations like limiting the Electron Flow, Signal Amplification, Signal Processing, Voltage Regulation, and Energy storage. These components are smaller in size and easier to carry.
Soldering all the components on a flat insulating material board is generally termed as a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) or Printed Wiring Board (PWB). Through this, electric current flows between all the components in the circuit.
Electronic Components are categorized into Two types.
- Passive Components.
- Active Components.
1. Passive Components

Passive Components are also called as Energy acceptors that do not control the current flow but affect the current flow.
- For their functioning, an external power supply is not needed.
- These components have low gain and are not used for signal amplification, power gain, and power amplification.
- Due to resistance, electrical energy is converted to heat and rotation.
Furthermore, Passive Electronic components three types, they are
- Resistor
- Capacitor, and
- Inductor
a) Resistor:
- Resistors are lossy or dissipative passive electronic components that help in restricting the current flow.
- This component is used for terminating the transmission lines and adjusting signal levels.
- It is indicated by the letter R.
- Resistance (R) is measured in Ohms (Ω).
Resistor types and their applications:
1. Linear Resistors
i) Fixed Linear Resistors
ii) Variable linear resistors
2. Non-linear Resistors
i) Thermistors
ii) Varistor
iii) Photo Resistors
b) Capacitors:
- The lossless passive electronic components that accumulate electric charge are called Capacitors.
- The electric charge is stored between two conductive plates and acts like an insulator called a dielectric. Dielectric materials will cause changes in the value of capacitance.
- It is indicated by the letter C.
- Farads (F) are the units of Capacitance (C).
Types of Capacitors
i) Electrolytic Capacitors
ii) Ceramic Capacitors
iii) Film Capacitors
iv) Variable Capacitor
v) Power Film Capacitors
vi) Paper Capacitors
c) Inductors:
- Based on its geometrical field shape, the energy is stored as Magnetic Flux around a coil from electric current.
- Its strength is based on the current, number of terms, and core materials, and is primarily developed to resist the current flow.
- These inductors are widely used in filters and transformers.
- It is denoted by the letter L.
- The Units of Inductance (L) is Henry (H).
Classification of inductors
The below classification is based on the core material used.
i) Iron Core Inductors
ii) Air Core Inductors
iii) Iron Powder Core Inductors
iv) Ferrite Core Inductors
2. Active Components:

Active components are those which need an external power source to operate. With these components, electrical current flow will be controlled and influenced.
- The energy supply to the circuit is done with the help of Active Components, due to which these components are called as Energy Donors.
- Signal processing for weak signals including amplification, and providing electricity to the circuit are the major applications of these components.
Types of Active Components:
- Diodes
- Transistors
- IC (Integrated Circuits)
a) Diodes
- These are defined as two-terminal components or components with two electrodes that allow the current to flow in a single direction.
- It also controls the current flow.
- These will work in two regions namely, Forward and Reverse Bias Regions.
- Diodes are mainly used in AC to DC conversion and Voltage spike reduction.
Types of Diodes
i) Light Emitting Diode
ii) Laser diode
iii) Avalanche diode
iv) Zener diode
v) Schottky diode
vi) Photodiode:
vii) PN junction diode:
b) Transistors:
- It is a three-terminal semiconductor device that helps in the conversion of a low-resistance signal to high resistance.
- It helps in either controlling or regulating the current flow or voltage.
- This type of device performs both amplification and rectification.
- The three terminals of the semiconductor are the Emitter, Base, and Collector. It can be used as a switch and an Amplifier.
Transistors are classified into two types. They are:
i) Bipolar Junction Transistor:
- NPN Transistor
- PNP Transistor
ii) Field Effect Transistor:
- Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFETs)
- The Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)
- Enhancement MOSFETs
- Depletion MOSFETs
c) IC (Integrated Circuits):
- Integrated circuits (ICs) are defined as the miniatured electronic components which include transistors, diodes, resistors, capacitors, and other components that are fabricated on a single semiconductor substrate, also called a Silicon chip.
- An IC can accumulate up to millions of electronic components on a single chip.
- After the development of ICs, the overall circuit size and power consumption were reduced.
Classification of ICs:
i) Based on integration level:
- Small Scale Integration (SSI)
- Medium Scale Integration (MSI)
- Large Scale Integration (LSI)
- Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI)
- Ultra Large Scale Integration (ULSI)
ii) Based on its application
- Linear integrated circuits
- Digital integrated circuits
iii) Based on its technology
- Monolithic technology
- Hybrid technology
Note: Learn about each type of component in detail in the upcoming articles. Stay Tuned!
Article By:
Navya Kommera
VLSI Design Engineer